About Department
Bridging Healthcare & Technology
The Department of Biomedical Engineering was established in the year 2020 with an intake of 60 to address the prevailing health sector challenges. This four year degree programme will nurture the young minds with fundamental knowledge of Biological sciences such as Human Anatomy, Physiology, Pathology and Microbiology. With this the student would also gain knowledge about Electronics, Measurements and Instrumentation to Design, Analyze, Synthesize and Evaluate the Diagnostic and Therapeutic equipments such as X-ray, CT, MRI, PET, Ventilators, Pacemakers, Dialyzer to serve the Medical community. The students will be guided to have periodical visits to the hospitals for bridging the gap between the class room learning and the real time issues.





Prosthetic devices for the physically challenged, Therapeutic equipments to replace the conventional medicines will also be part of the learning to this stream of engineers. This department has a well established relationship with industrial experts and physicians of different expertise to keep it updated and live up to the expectations of the contemporary world.
Through “ZYGOTE” association, the department organizes Guest Lectures, Workshops and Seminars on recent trends to enhance the technical knowledge and equip the skills of students. A committee on Anti-Drugs arranges awareness programs at regular intervals to address the adverse effects. Students are appreciated to have exposure to on field trainings like Hospital Training, Industrial Visits, Internships, NPTEL courses, IIT spoken tutorials, Value Added Courses and Onsite projects in various reputed organizations.
The department has signed 2 MoUs with organizations like Thangam Hospital – Namakkal and Mothercell Regenerative Private Limited (MRC) – Tiruchirappalli to carry out Faculty Training Programs, Internship/Industrial Visit/In-Plant, Hospital Training, Projects and Consultancy.
Overview
Vision & Mission
VISION
To create biomedical engineering graduates through value based education and research with
high ethical standards and ensuring professionalism in the health care industry.
MISSION
- Educating the learner to understand the principle, operation, design and application of biomedical instrumentation, electronics and measuring of biomedical signals in human being
- Creating an interdisciplinary learning environment to conceive new ideas.
- Developing competency for employability and entrepreneurship in core and interdisciplinary areas.
PEOs, PSOs and POs
PROGRAM EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE (PEOs)
- PEO I : Graduates shall be leaders in generating innovative knowledge at the interface of Biology and Engineering.
- PEO II : Graduates will show excellence in leadership skills, design, and model new equipments needed for health care and serve the society.
- PEO III : Graduates will demonstrate ethical standards, leadership skills, attitude, professional responsibilities, contribute positively to team building and keep themselves engaged in lifelong learning.
PROGRAM SPECIFIC OUTCOMES (PSOs)
- PSO1 Professional Skills : Students shall be able to measure, model, manipulate, and make biological systems for powerful new biological technologies.
- PSO2 Competency : Students shall be able to apply the concepts of signal and image processing techniques to address the problems of healthcare.
PROGRAM OUTCOMES (POs)
- Engineering Graduates will be able to :
- Engineering knowledge : Apply the knowledge of mathematics, science, engineering fundamentals, and an engineering specialization to the solution of complex engineering problems.
- Problem analysis : Identify, formulate, review research literature, and analyze complex engineeriCng problems reaching substantiated conclusions using first principles of mathematics, natural sciences, and engineering sciences.
- Design/development of solutions : Design solutions for complex engineering problems and design system components or processes that meet the specified needs with appropriate consideration for the public health and safety, and the cultural, societal, and environmental considerations.
- Conduct investigations of complex problems : Use research-based knowledge and research methods including design of experiments, analysis and interpretation of data, and synthesis of the information to provide valid conclusions.
- Modern tool usage : Create, select, and apply appropriate techniques, resources, and modern engineering and IT tools including prediction and modeling to complex engineering activities with an understanding of the limitations.
- The engineer and society : Apply reasoning informed by the contextual knowledge to assess societal, health, safety, legal and cultural issues and the consequent responsibilities relevant to the professional engineering practice.
- Environment and sustainability : Understand the impact of the professional engineering solutions in societal and environmental contexts, and demonstrate the knowledge of, and need for sustainable development.
- Ethics : Apply ethical principles and commit to professional ethics and responsibilities and norms of the engineering practice.
- Individual and team work : Function effectively as an individual, and as a member or leader in diverse teams, and in multidisciplinary settings.
- Communication : Communicate effectively on complex engineering activities with the engineering community and with society at large, such as, being able to comprehend and write effective reports and design documentation, make effective presentations, and give and receive clear instructions.
- Project management and finance : Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the engineering and management principles and apply these to one’s own work, as a member and leader in a team, to manage projects and in multidisciplinary environments.
- Life-long learning : Recognize the need for, and have the preparation and ability to engage in independent and life-long learning in the broadest context of technological change.
Facilities
DIAGNOSTIC AND THERAPEUTIC EQUIPMENT LABORATORY
A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Equipment Laboratory is a specialized facility dedicated to the testing, and evaluation of medical devices used in diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. These labs are crucial in ensuring the safety, accuracy, and effectiveness of medical equipment in the healthcare sector.
- Diagnostic Equipment : Diagnostic equipment refers to the devices used to detect, diagnose, and monitor various medical conditions. These tools provide healthcare professionals with necessary information required to monitor a patient & health, enabling accurate diagnosis and timely treatment.
- Therapeutic Equipment : Therapeutic equipment refers to devices used in the treatment of various medical conditions. These devices help to manage and alleviate pain, improve patient outcomes, and support recovery.

| S.No | Description of Equipment | Required numbers
(for batch of 30 students) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | pH meter and conductivity meter | 1 |
| 2 | Photo transducer for pulse measurement | 1 |
| 3 | Sphygmomanometer and Stethoscope | 1 |
| 4 | Blood flow measurement system | 1 |
| 5 | Multiparameter (ECG, EMG, EEG) Simulator | 2 |
| 6 | Function Generator | 8 |
| 7 | DSO | 8 |
| 8 | Regulated Power Supplies | 8 |
| 9 | Bread boards | 8 |
| 10 | IC LM 324 | 20 |
| 11 | AD 620 | 20 |
| 12 | INA series (126, 128 …) | 20 |
| 13 | 555 Timer | 1 |
| 14 | Opto Isolator IC: MCT2E | 1 |
| 15 | Software tool for PCB design | 1 |
| 16 | Visually evoked potential setup | 1 |
| 17 | GSR setup | 1 |
| 18 | Multi output power supply (+15V, -15V, +30V Variable, +5V, 2A) | 2 |
| 19 | Shortwave Diathermy | 1 |
| 20 | Ultrasound Diathermy | 1 |
| 21 | Multiparameter biotelemetry system | 1 |
| 22 | Electrical Safety Analyzer | 1 |
| 23 | Spirometry with associated analysis system | 1 |
| 24 | ECG Simulator | 1 |
| 25 | Medical Stimulatory | 1 |
| 26 | Surgical diathermy with analyzer | 1 |
| 27 | Audiometer | 1 |
| 28 | Pacemaker | 1 |
| 29 | Defibrillator | 1 |
| 30 | Haemodialysis model | 1 |
| 31 | Heart lung machine | 1 |
| 32 | Ultrasound scanner | 1 |
| 33 | Ventilator | 1 |
BIOSCIENCES LABORATORY
The role of laboratories in biosciences is indeed vital for enhancing our understanding of life at the molecular, cellular, and organism levels. These laboratories serve as hubs for scientific discovery, innovation, and diagnostics in a wide range of biological fields, from molecular biology to medical sciences.
| S.No | Description of Equipment | Required numbers
(for batch of 30 students) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Weighing Balance | 1 |
| 2 | pH Meter | 2 |
| 3 | UV-Vis Spectrophotometer | 2 |
| 4 | Water Bath | 2 |
| 5 | Sonicator | 1 |
| 6 | Centrifuge | 1 |
| 7 | BTS Semi Auto Analyzer | 1 |
| 8 | Colorimeter | 2 |
| 9 | Microscope With USB Camera Eye Piece | 1 |
| 10 | Magnetic Stirrer | 1 |
| 11 | Hot Air Oven | 2 |
| 12 | Incubator | 1 |
| 13 | Autoclave | 2 |
| 14 | Laminar Air Flow | 1 |
| 15 | Refrigerator | 1 |
| 16 | TLC- Applicator, Plates, Chamber | 1 |
MEDICAL IMAGE PROCESSING LABORATORY
A Medical Image Processing Lab is a specialized laboratory focused on using computational techniques to analyze and interpret medical images. These labs typically deal with images obtained from various medical imaging modalities such as X-rays, CT (Computed Tomography) scans, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), ultrasound, and PET (Positron Emission Tomography). It has involved in the various techniques of Image Enhancement, segmentation and visualization. It has played a major role in filtering, edge detection, histogram equalization, and noise removal. Methods like thresholding, region-growing. The goal of medical image processing is to enhance the quality of these images, extract meaningful information, and assist healthcare professionals in diagnosing, monitoring, and treating medical conditions. Python& MATLAB are widely used for developing algorithms and processing medical images.
| S.No | Description of Equipment | Required numbers
(for batch of 30 students) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Personal Computer | 30-Nos |
| 2 | MATLAB software |

clinical diagnosis laboratory
A clinical diagnosis laboratory is a facility that performs tests on biological samples (such as blood, urine, tissues, or other bodily fluids) to help diagnose and monitor diseases. It is an essential facility for biomedical students to understand, as it bridges the gap between biological sciences and clinical applications. Biomedical students should familiarize themselves with essential lab equipment such as hematology analyzers, spectrophotometers, centrifuges, PCR machines, automated chemistry analyzers, microscopes, and flow cytometers. Biomedical engineers play a significant role in designing, innovating, calibrating, and maintaining lab equipment to ensure precision and efficiency, while also integrating automation and troubleshooting technical issues. These labs adhere to stringent quality control protocols, including regular checks and ISO/NABL accreditation to ensure test accuracy.

| S.No | Description of Equipment | Required numbers
(for batch of 30 students) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Medical Microscope | 2 |
| 2 | Medico Centrifuge | 1 |
| 3 | Spectrophotometer | 1 |
| 4 | LX-200 LED Binocular Microscope | 1 |
| 5 | General Purpose Centrifuge | 1 |
| 6 | Haemoglobinometer | 4 |
| 7 | Ophthalmoscope | 2 |
| 8 | Tuning Fork | 8 |
| 9 | Electronic Weighing Balance | 1 |
| 10 | Mono Quartz Distillation | 1 |
| 11 | Paraffin Dispenser | 1 |
| 12 | Colorimeter | 1 |
| 13 | UV -VIS | 1 |
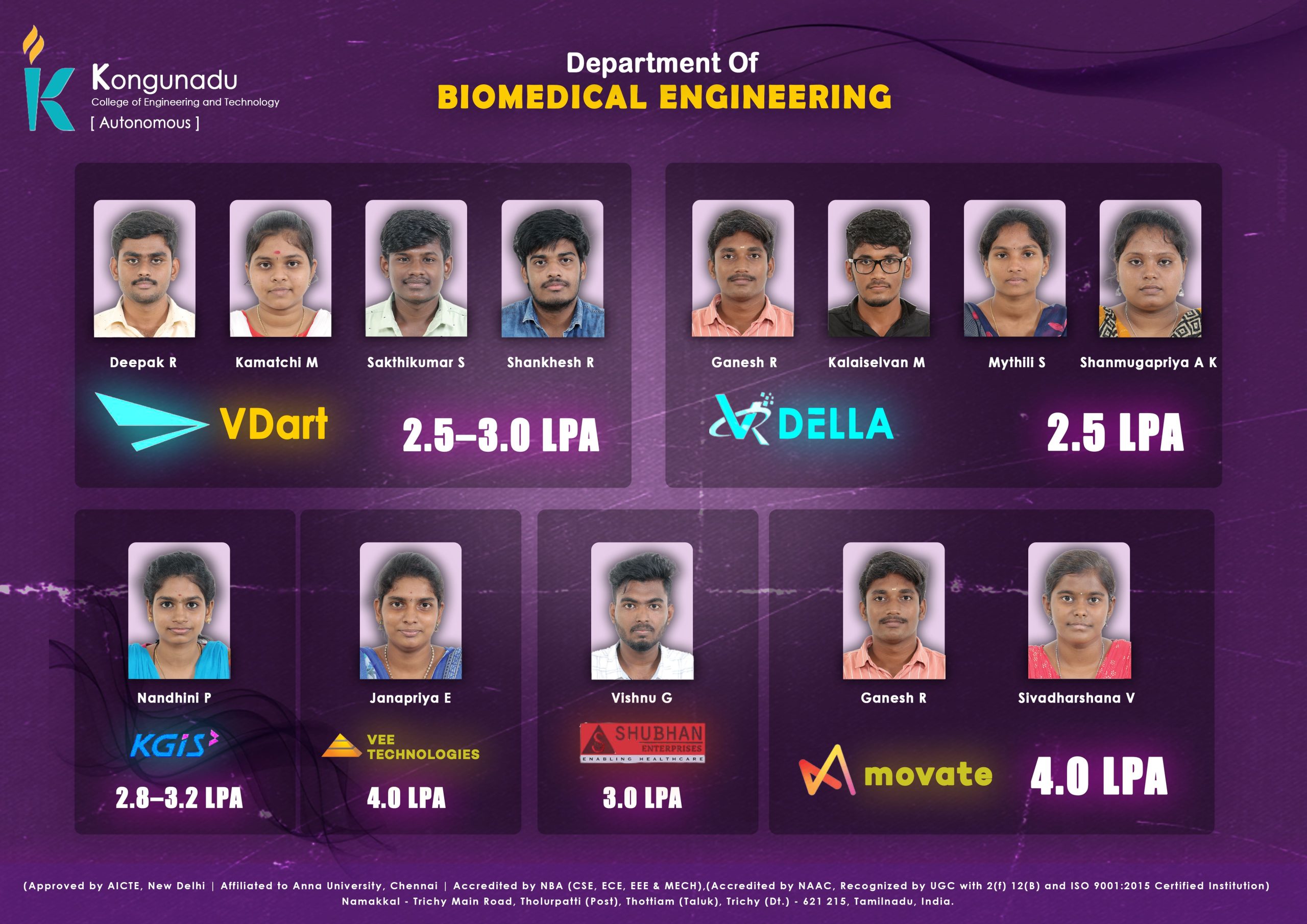
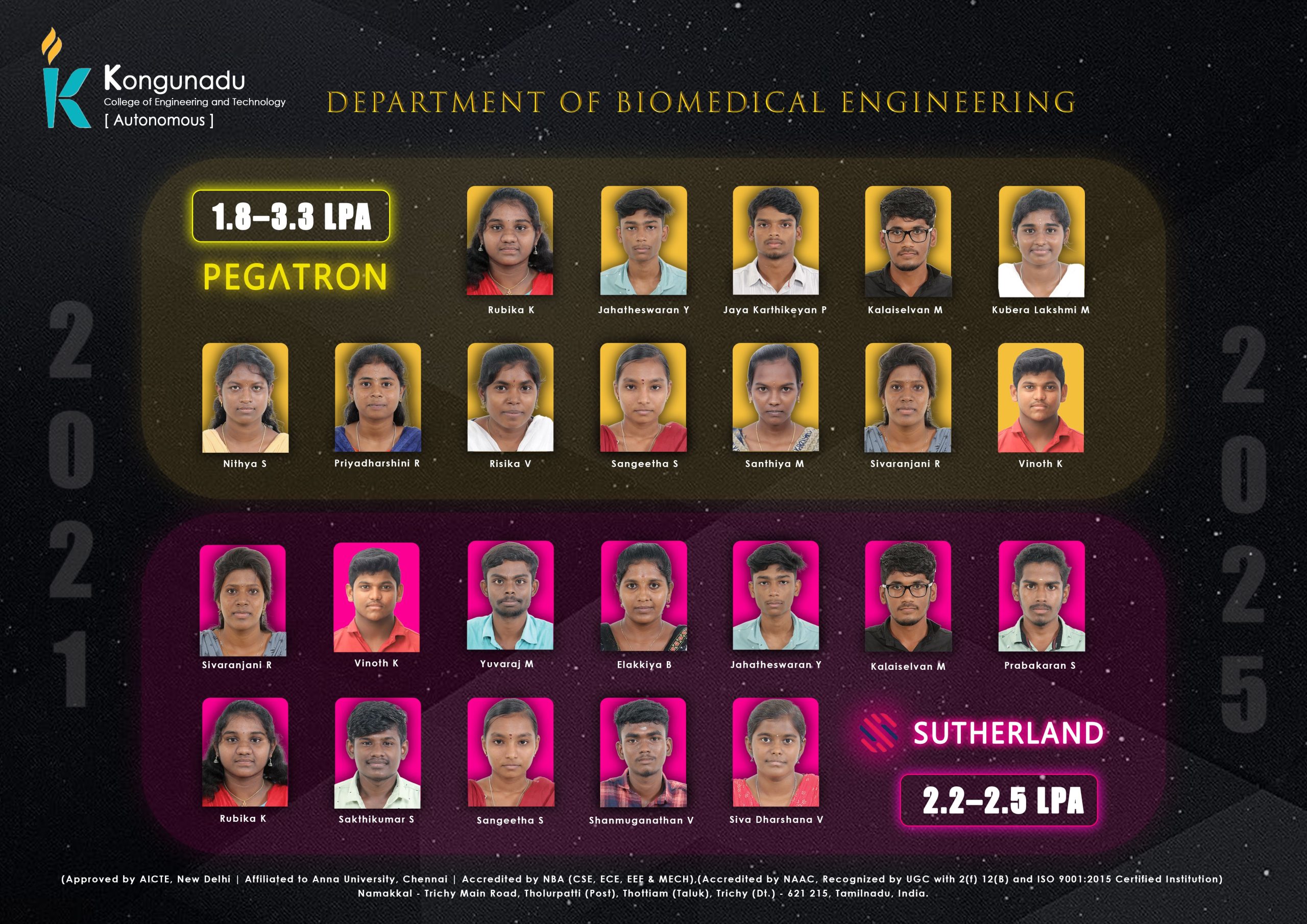
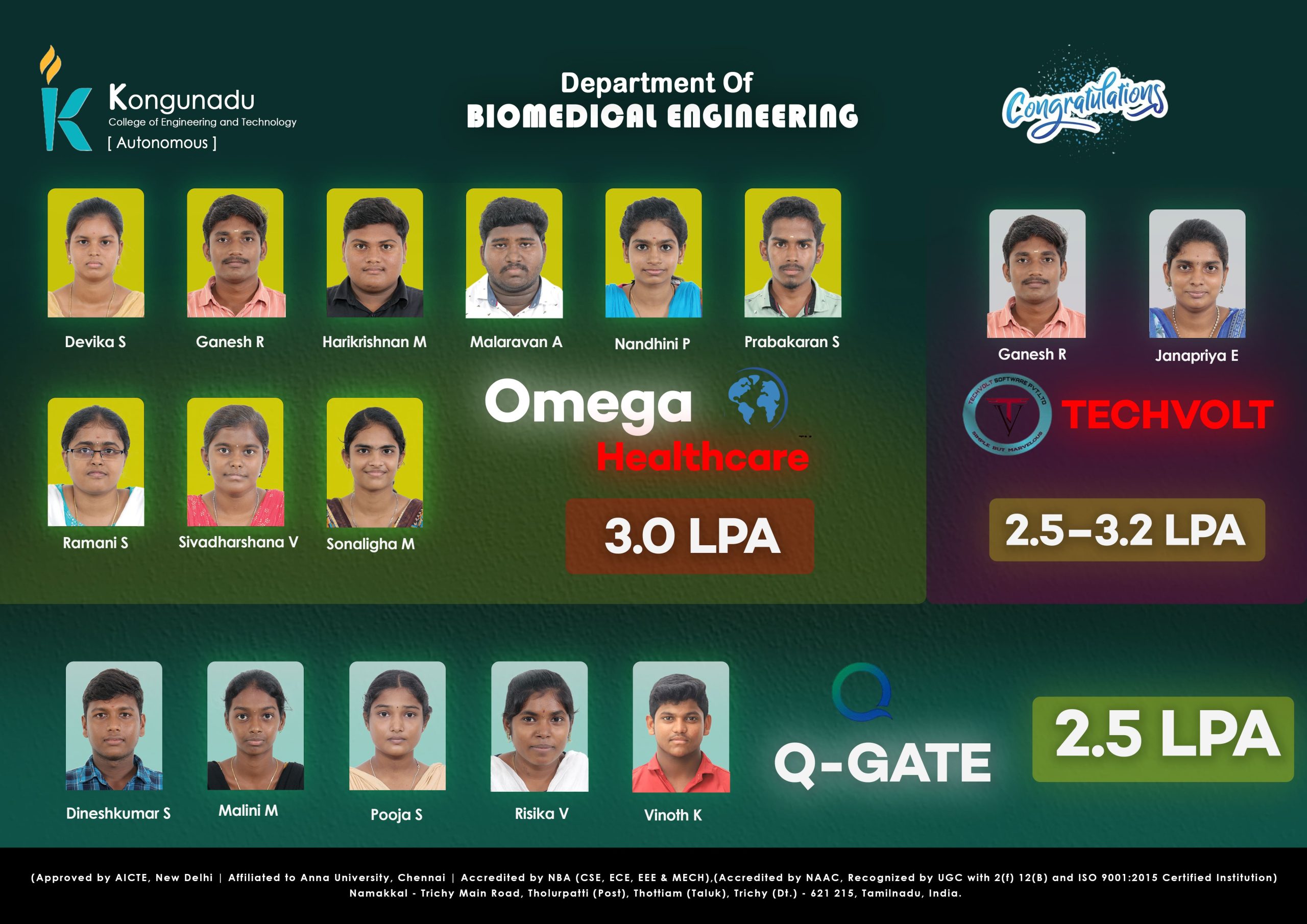
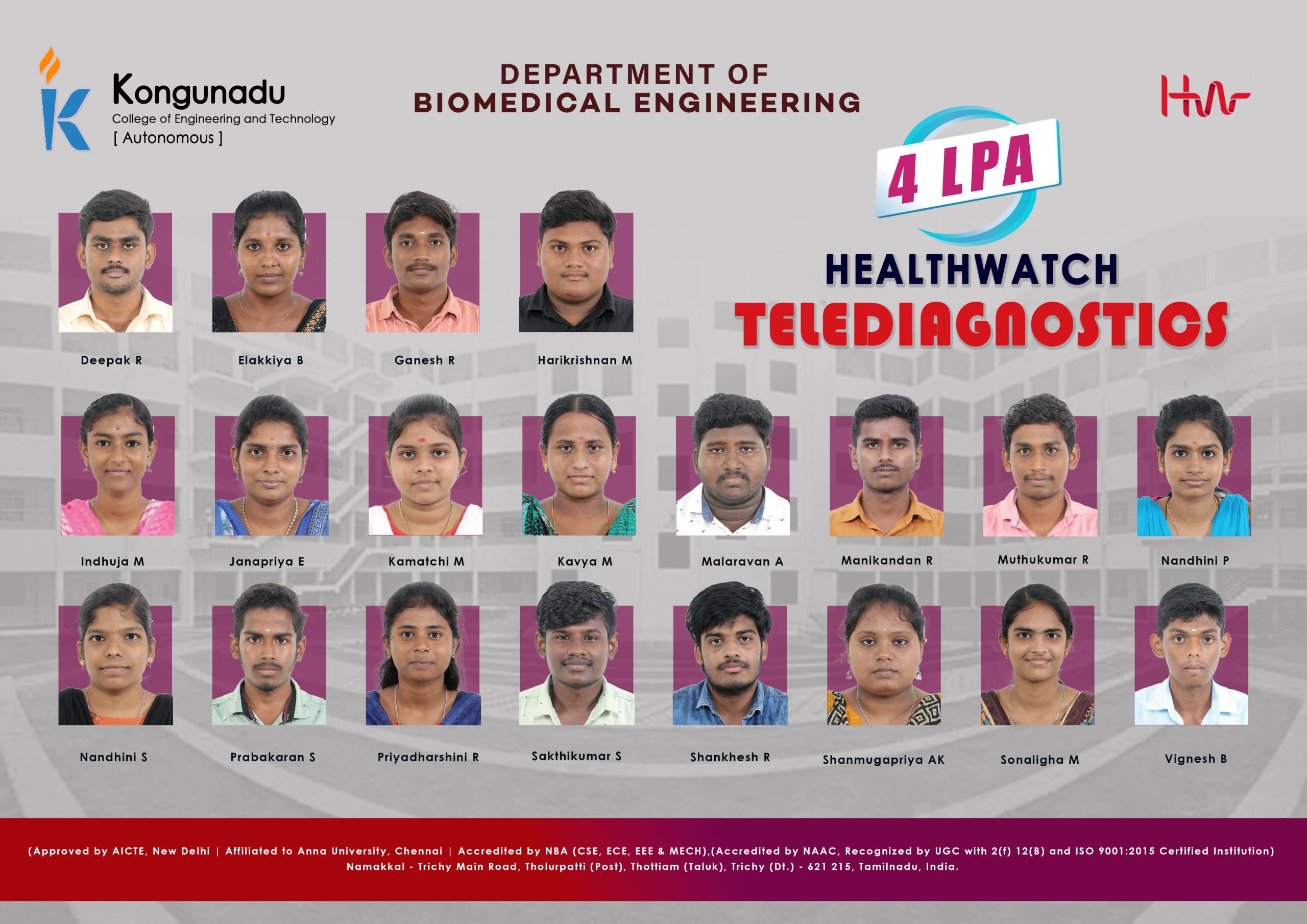
Placement Details
Industrial Training - Faculty
Funds Received
Newsletter & Magazine
Faculty Members
Faculty Members
| S.No | Name of the Faculty | Designation | Qualification | Nature of Association (Regular/Contractual/Adjunct) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dr. T. Ashok | Associate Professor / HoD | M.Tech., Ph.D | Regular |
| 2 | Dr. P. Elamurugan | Professor | M.E., Ph.D | Regular |
| 3 | Mr. T. Muthukumar | Assistant Professor | M.E., (Ph.D) | Regular |
| 4 | Mr. R. Pandu Rangan | Assistant Professor | M.E | Regular |
| 5 | Mr. K. Bashkaran | Assistant Professor | M.E., (Ph.D) | Regular |
| 6 | Mr. R. Ragul Kannan | Assistant Professor | M.E., (Ph.D) | Regular |
| 7 | Ms. K. Brintha | Assistant Professor | M.E | Regular |
| 8 | Mr. M. Arunkumar | Assistant Professor | M.E | Regular |
| 9 | Ms. S. Priyadharshini | Assistant Professor | M.E | Regular |
| 10 | Ms. U.K. Subhiksha | Assistant Professor | M.E | Regular |
| 11 | Mr. S. Sethuragavan | Assistant Professor | M.E | Regular |
Supporting Staff
| S.No | Name of the Faculty | Designation | Qualification | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mrs. G. Maheshwari | Lab Assistant | B.Sc., DMLT | ||
| 2 | Mrs. V. Dhivya | Lab Assistant | BSS Nursing | ||
| 3 | Mrs. G. Kousalya | Technical Assistant | B.E |
| S.No | Subject Code | Subject Name | Question Bank | Handouts | Lecture Video |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 24MA303 | Transforms and Partial Differential Equation | Download |
|
|
| 2 | 24BM301 | Human Anatomy and Physiology | Download |
|
|
| 3 | 24BM302 | Medical Physics | Download |
|
|
| 4 | 24EC201 | Digital Principles and System Design | Download |
|
|
| 5 | 24BM303 | Electrical Engineering for Biomedical | Download |
|
|
| 6 | 24AD201 | Python Programming | Download |
|
|
II Year- III Semester
| S.No | Subject Code | Subject Name | Question Bank | Handouts | Lecture Video |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 24MA303 | Transforms and Partial Differential Equation | Download |
|
|
| 2 | 24BM301 | Human Anatomy and Physiology | Download |
|
|
| 3 | 24BM302 | Medical Physics | Download |
|
|
| 4 | 24EC201 | Digital Principles and System Design | Download |
|
|
| 5 | 24BM303 | Electrical Engineering for Biomedical | Download |
|
|
| 6 | 24AD201 | Python Programming | Download |
|
|
REGULATIONS 2020
II Year- VI Semester
II Year- V Semester
II Year- IV Semester
II Year- III Semester
Exit Survey
Analysis of Feedback on Facilities

Find your Future at Kongunadu
Achieve academic excellence with expert mentorship, hands-on learning, and a vibrant campus life—all at an affordable cost. Prepare for a successful and innovative career!

















